Overview
This guideline covers diagnosing and managing Lyme disease. It aims to raise awareness of when Lyme disease should be suspected and ensure that people have prompt and consistent diagnosis and treatment. It does not cover preventing Lyme disease.
In October 2018, we corrected the information in table 2 relating to treatments for Lyme carditis in children aged 9 to 12 who are haemodynamically unstable.
Recommendations
This guideline includes recommendations on:
- being aware of Lyme disease
- symptoms and history taking
- which tests to use and when
- treatment with antibiotics
- treatment and support for ongoing symptoms
- managing Lyme disease in pregnant women and their babies
- information for people with Lyme disease
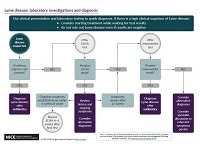
See a visual summary of the recommendations on testing for Lyme disease.
Who is it for?
- Healthcare professionals including GPs, nurses, specialists and microbiologists
- Commissioners and providers
- People with Lyme disease, their families and carers
Guideline development process
How we develop NICE guidelines
Your responsibility
The recommendations in this guideline represent the view of NICE, arrived at after careful consideration of the evidence available. When exercising their judgement, professionals and practitioners are expected to take this guideline fully into account, alongside the individual needs, preferences and values of their patients or the people using their service. It is not mandatory to apply the recommendations, and the guideline does not override the responsibility to make decisions appropriate to the circumstances of the individual, in consultation with them and their families and carers or guardian.
All problems (adverse events) related to a medicine or medical device used for treatment or in a procedure should be reported to the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency using the Yellow Card Scheme.
Local commissioners and providers of healthcare have a responsibility to enable the guideline to be applied when individual professionals and people using services wish to use it. They should do so in the context of local and national priorities for funding and developing services, and in light of their duties to have due regard to the need to eliminate unlawful discrimination, to advance equality of opportunity and to reduce health inequalities. Nothing in this guideline should be interpreted in a way that would be inconsistent with complying with those duties.
Commissioners and providers have a responsibility to promote an environmentally sustainable health and care system and should assess and reduce the environmental impact of implementing NICE recommendations wherever possible.