Overview
This guideline covers care and management for adults (aged 18 and over) with type 2 diabetes. It focuses on patient education, dietary advice, managing cardiovascular risk, managing blood glucose levels, and identifying and managing long-term complications.
For information on related topics, see our cardiometabolic disease prevention and treatment summary page.
Last reviewed: 23 December 2024
We are updating our recommendations on drug therapy (excluding insulin-based treatments). See the guideline in development page for progress on the update.
This guideline updates and replaces:
- NICE guidelines CG66 (published May 2008) and CG87 (published May 2009)
- NICE technology appraisal guidance 203 and 248
- NICE evidence summaries ESNM20, ESNM26 and ESNM59.
Portfolio review in May 2023: We have reviewed our guidelines portfolio to identify topics that we think will add the most value to the health and care system and have agreed the update on insulin therapy recommended in this surveillance report will not proceed as planned.
How we prioritise updating our guidance
Decisions about updating our guidance are made by NICE’s prioritisation board. For more information on the principles and process, see NICE-wide topic prioritisation: the manual.
For information about individual topics, including any decisions affecting this guideline, see the summary table of prioritisation board decisions.
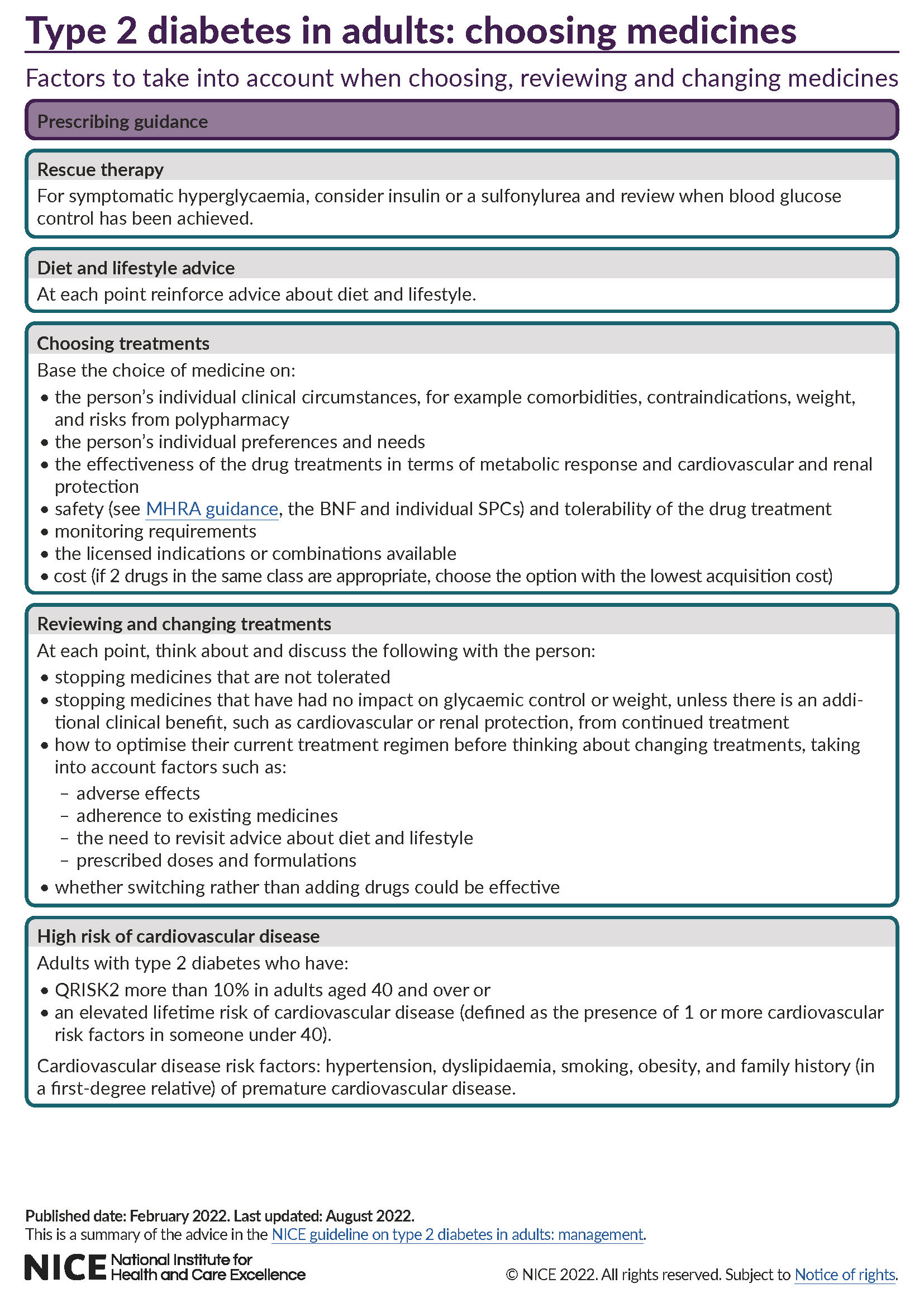
Recommendations
This guideline includes recommendations on:
- individualised care
- managing blood glucose levels, including HbA1c measurement and targets
- first-line drug treatment
- reviewing drug treatments
- treatment options if further interventions are needed
- antiplatelet therapy
- managing complications
For recommendations on hypertension in people with type 2 diabetes, see the NICE guideline on hypertension in adults.
Who is it for?
- Healthcare professionals
- Commissioners and providers
- Adults with type 2 diabetes, and their families and carers
Guideline development process
How we develop NICE guidelines
Your responsibility
The recommendations in this guideline represent the view of NICE, arrived at after careful consideration of the evidence available. When exercising their judgement, professionals and practitioners are expected to take this guideline fully into account, alongside the individual needs, preferences and values of their patients or the people using their service. It is not mandatory to apply the recommendations, and the guideline does not override the responsibility to make decisions appropriate to the circumstances of the individual, in consultation with them and their families and carers or guardian.
All problems (adverse events) related to a medicine or medical device used for treatment or in a procedure should be reported to the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency using the Yellow Card Scheme.
Local commissioners and providers of healthcare have a responsibility to enable the guideline to be applied when individual professionals and people using services wish to use it. They should do so in the context of local and national priorities for funding and developing services, and in light of their duties to have due regard to the need to eliminate unlawful discrimination, to advance equality of opportunity and to reduce health inequalities. Nothing in this guideline should be interpreted in a way that would be inconsistent with complying with those duties.
Commissioners and providers have a responsibility to promote an environmentally sustainable health and care system and should assess and reduce the environmental impact of implementing NICE recommendations wherever possible.